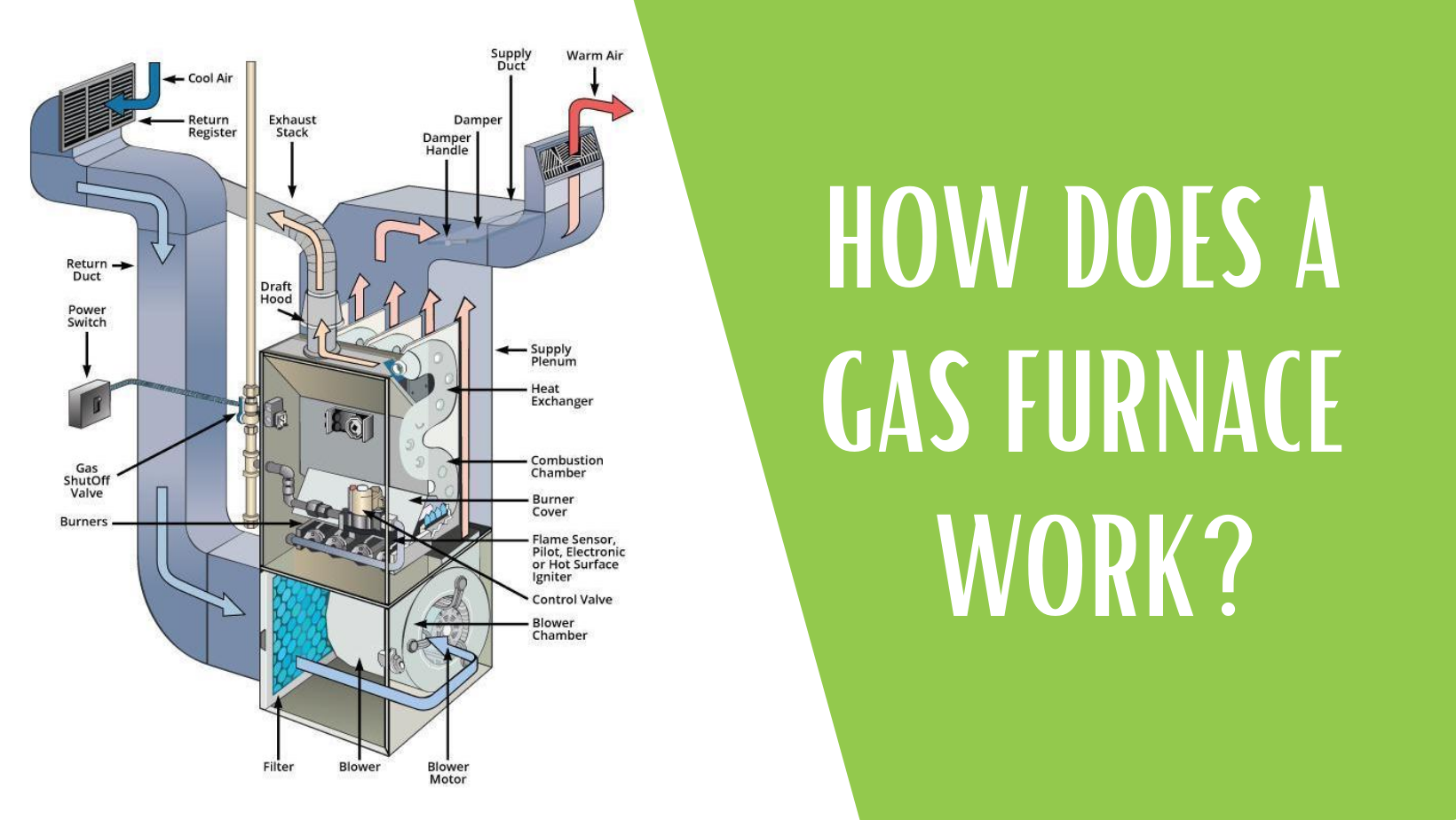
Ever wonder how your central heating system works to keep you warm in those winter months? Maybe you're buying a new gas furnace and want to know all about the different components and efficiency options. Either way, here's all you need to know about how a central gas furnace works.
The Process
Simply put, a central gas heating system creates a cycle of generating heat to increase the temperature of cooler air in the home. Here's a basic version of how it works:
- Burning propane or natural gas generates heat in the furnace's burner.
- The heat produced passes through a heat exchanger, making it hot.
- Air from the home's return ductwork is blown over the heat exchanger, warming the air.
- The furnace's blower then forces the heated air through the supply ductwork, distributing it throughout the home.
Components of a Gas Furnace
Here are the main components of a gas furnace and how they work together to provide heat to your home:
-
Temperature Control: The temperature control, which is regulated by the furnace control board, turns on the ignition switch and starts the heating process when the thermostat or control system calls for heat.
-
Gas Burners: When the thermostat or control system calls for heat, the gas burners valves are open to deliver gas and burn fuel.
-
Ignition Switch: Gas flows over the igniter to establish a flame. This flame is drawn through the burners and used to heat the heat exchanger.
-
Induced Draft Fan: The induced draft fan draws air into the burner assembly. The air allows the burners to warm the heat exchanger.
-
Heat Exchanger: The part of a gas furnace that adds heat to the indoor air. The gas combusts inside the heat exchanger, creating heat that is used to heat the passing air. The design of a heat exchanger can add energy-efficient operation of a gas furnace.
-
Blower Motor: Uses the return venting to blow air over the hot heat exchanger. The warmed air is then sent throughout your home via ductwork and supply vents. Some furnace models offer a blower fan that can run at multiple speeds to improve efficiency.
-
Flue: A flue or chimney acts as an exhaust for gaseous by-products of combustion used to create heat.
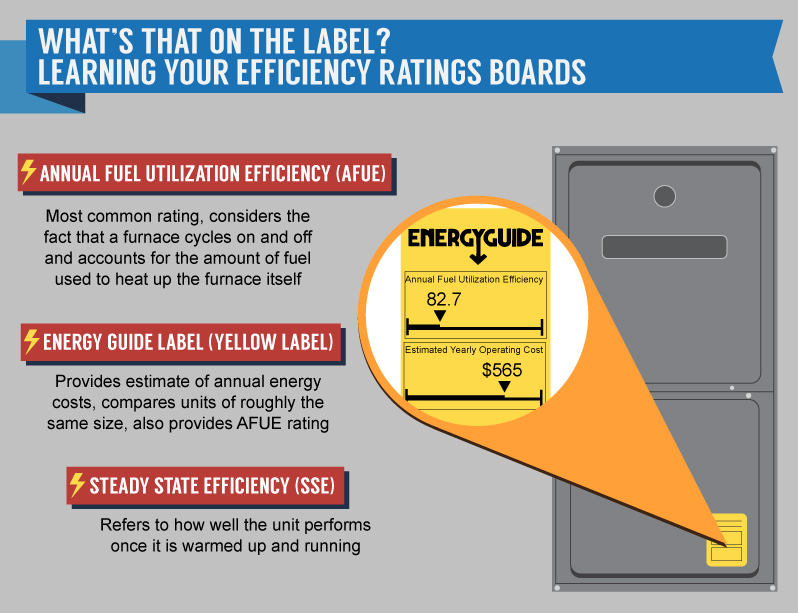
Energy-Efficiency
There are two main types of gas furnaces for homeowners to choose from when it comes to AFUE rating: condensing and non-condensing. The higher the AFUE, the higher the efficiency.
Non-condensing gas furnaces (80% AFUE)
This type of furnace has only one heat exchanger. Inside the heat exchanger, fuel combusts to release heat. During this combustion process, some of the heat produced is lost and turned into water vapor and exhaust gases. These gases are carried out of the furnace via the flue pipe, which is basically a chimney that sends gases into the outside air.
All of this means that a standard, non-condensing gas furnace wastes a decent amount of fuel and potential heat in the form of exhaust gases.
Condensing gas furnace (90%-98% AFUE)
A condensing gas furnace combats the issue of wasted energy through the use of a second heat exchanger. The second one works to take that water vapor and exhaust gas and extract more heat out of those fumes. By using a more energy-efficient system, you will also save on heating bills. You can read more about the difference between non-condensing and condensing gas furnaces here.
Single-Stage vs. Two-Stage vs. Modulating
A single-stage gas furnace is characterized by one constant flow of gas. It can either be set to ON or OFF -- there is no adjusting the gas flow.
A two-stage gas furnace has a HIGH and LOW setting on the gas burner. This allows for two levels of operation: full gas flow for more heat and lower flow for milder days.
A multi-stage or modulating gas furnace continuously regulates the amount of fuel burned to maintain the set temperature of your thermostat.
You can read more about the difference between these three types of furnaces here.
If you live in the Delaware Valley/Greater Philadelphia area and would like to find comfort within your home, visit our website or give us a call at 215 - 245 - 3200 to learn more.