If you're looking to add heating or upgrade your current home heating system, it may be tough to know where to start. Is there ductwork in place? Is the house currently being built? Are you looking for energy efficiency? How much do you want to spend? What are all the options?!
These are all questions you'll need the answer to, so we laid out the answer to the last one. There are seven types of home heating systems, all explained below.
Furnace (forced-air distribution system)
Simply put, furnaces work by igniting the gas, propane, or oil in the burner/chamber. The flames heat up a metal heat exchanger which transfers the heat through ducts to be distributed throughout the home. As warm air fills each room, the colder air is drawn back into the furnace via return ducts, then the cycle repeats. Furnaces are considered central air systems because the heat is generated in a central area of the home and the sent through the house.
Advantages
Furnaces (forced air systems) can be filtered to remove dust and allergens, can have humidifiers/dehumidifiers integrated, and are relatively inexpensive.
Disadvantages
Furnaces require ductwork, take up more space, and can be noisy.
Boiler
Boilers are another common heating system. They work by heating water in a storage tank and sending hot water or steam through pipes to provide heating. The energy source used to heat the liquid can be electricity, oil, or natural gas. While boiler systems allow you to practice zoned heating, they are also significantly more expensive to install and cost more money to run compared to other heating systems. There are two main ways a boiler can be made up.
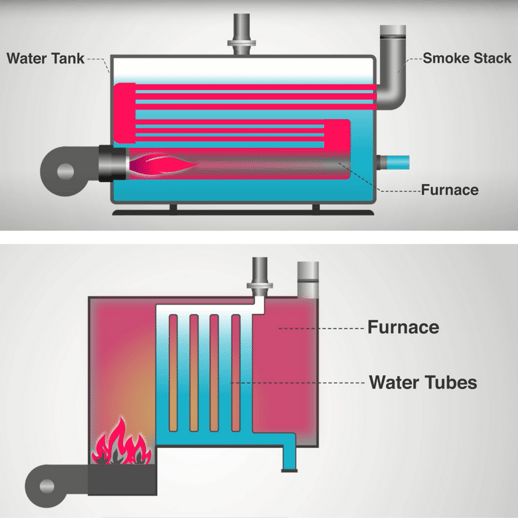
Fire-tube boilers (top) are typically made up of a furnace, a water tank acting as a boiler, and a smokestack. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, then the tube transfers the heat of the furnace through the water in the tank. Steam is then generated and moved downstream. Fire-tube boilers tend to be the cheapest to produce due to their relatively simple construction, but are typically limited to low to medium pressure applications.
Water-tube boilers (bottom) are similar, but instead of the furnace heating fire tubes to heat water in the tank, the furnace directly heats water tubes inside of the furnace. Steam is then generated and moved downstream. This type of boiler is the more efficient option.
To put it simply: in a fire-tube boiler, the fire or hot gas is present inside the tubes with water surrounding the fire tubes. In a water-tube boiler, the water is present inside the tubes and fire or hot gases surround these fire tubes.
Advantages
Water boilers are virtually silent and typically cost less to run than forced-air systems. There is also less routine maintenance for boilers (e.g. no filter change).
Disadvantages
Replacement parts for boilers can be more expensive to install than forced air systems. Boilers also can't be used for cooling, which means you will need a separate system. Plus, although it's not common, boilers present the risk of water leaks.
Heat Pump
There are three types of heat pumps: air-source, water-source, and geothermal. Air-source heat pumps are the most common type when it comes to home heating.
Heat pumps are really just two-way air conditioners; the biggest difference between a standard air conditioning system and a heat pump is that a heat pump can reverse its cycle to provide heating as well. Since standard units cannot reverse their cycle, they are often paired with furnaces to provide heat, creating a complete heating and cooling system.
Air-source heat pumps provide cooling by removing hot air in a room and sending it outside. To provide heat, they absorb thermal energy from the outside air then distribute it inside via ducts.
Heat pumps are a great option due to their efficiency, money-saving qualities, and their convenience in the case that ducts need to be extended. On the other hand, installing ductwork can be expensive and disruptive in an already-built home, and the possibility of leaky ducts can decrease efficiency and increase your energy bill. Additionally, standard heat pumps don't work well once the temperature dips too low.
Advantages
Heat pumps offer both heating and cooling and come in three types. All three types are much more efficient compared to traditional systems. Heat pumps also work with or without ductwork.
Disadvantages
Standard heat pumps only work in relatively mild climates and can be more expensive to install.
Hybrid Heating System
Since standard heat pumps cannot provide enough warmth in colder temperatures, they can be paired with a furnace to create a hybrid heating system. The heat pump can be used as a more efficient source during milder seasons, while the furnace can be used during extreme temperatures.
With this system, you aren’t just relying on one heating source, which means you will reduce significant strain on both units, thus reducing the need for repairs and replacements.
Advantages
Hybrid systems can increase efficiency because you can use the heat pump until it gets too cold and then switch to the furnace. Switching between two systems also means less strain on both.
Disadvantages
Hybrid systems have a higher upfront cost and does not use completely renewable energy resources.
Ducted and ductless hybrid
Another type of hybrid system can be combining both ducted and ductless (see below) indoor units for a heat pump system. The right system can provide flexibility and personalized comfort for you and your home. This is a good idea for homeowners who want to make use of existing ductwork while also adding ductless units for specific problem areas, additions, sunrooms, etc. where the ductwork will not reach or suffice.
Ductless Heat Pump
Ductless heat pumps are a type of air-source heat pump, and they can solve issues that are present with standard heat pumps. They work in the same way, but instead of transferring the heated or cooled air through ducts, the air is transferred through small line sets in walls that connect to air handlers in each room. Without the need for ductwork, these heat pump systems are much easier to install and are less invasive. However, the air handlers are mounted on walls and floors and can be seen, as opposed to ducts which are hidden behind walls.
Another upside of ductless heat pumps is that they can be your one and only heating source. For example, the Hyper-Heat heat pump from Mitsubishi Electric can provide heat in temperatures as low as negative 13 degrees Fahrenheit. With this type of heat pump, you would not need the addition of another heating source for colder temperatures.
Advantages
Ductless heat pumps are even more efficient than ducted because they allow for zoned heating and cooling. They require easy installations and no bulky ductwork is needed that would take up space.
Disadvantages
Ductless heat pumps only cool smaller spaces or more open-floor type areas. Some homeowners may not like the look of the air handlers visibly sticking out of walls, floors, and ceilings.
Radiant Heating
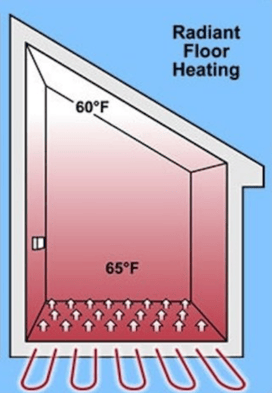 Radiant floor heating systems come in two varieties: a hydronic system and an electric system. Both types work by providing heat from the floor up. While a radiant heating distribution system can last a long time, repairs can become very expensive if a problem arises. The lifespan of radiant heat is dependent on its heat source system.
Radiant floor heating systems come in two varieties: a hydronic system and an electric system. Both types work by providing heat from the floor up. While a radiant heating distribution system can last a long time, repairs can become very expensive if a problem arises. The lifespan of radiant heat is dependent on its heat source system.
The heat source for a hydronic radiant floor system is a boiler centrally located in the home. The heat produced by the boiler is transferred to tubing carrying hot water beneath the home’s flooring.
With an electric system, heating coils are located beneath the floor rather than tubing. Electric systems are best used as an add-on in a specific room or area such as in a small bathroom, whereas hydronic systems are intended to heat an entire house.
Advantages
Radiant systems provide even, comfortable heat and can be very efficient. In-floor heating systems are also invisible and quiet.
Disadvantages
Radiant systems can be relatively slow to heat up and installation can be expensive. Boiler-based systems cannot be combined with air conditioning.
Radiant floor heating is not to be confused with radiators. Radiators use hot water or steam to heat their coils, which then warm the surrounding space through radiation and convection. Although radiators are quick to produce heat, they are typically used for space heating rather than whole-home heating, especially in bigger homes. Radiators are generally installed along the edge of outside walls, and some heat can be lost to the exterior of your home as heat radiates outwards.
Baseboard Heaters
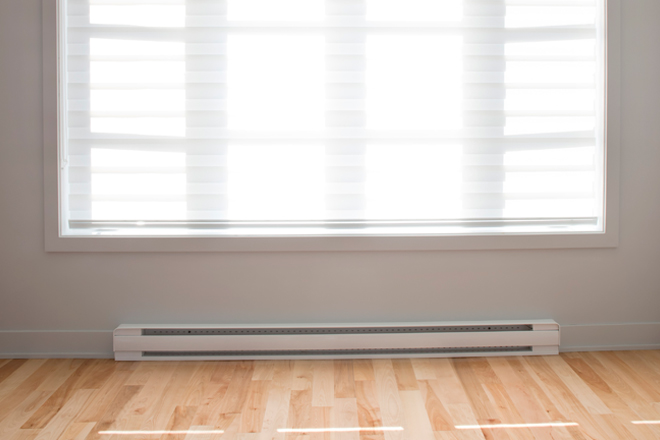

Baseboard heaters can also be electric or hydronic. Electric baseboard heating works through convection. Units are typically placed below windows, and as cold air falls from the window it enters the baseboard unit through a vent. Within the baseboard, the air is warmed by a series of metal fins that have been heated through electricity. The warm air then rises from the baseboard and the cycle continues, creating a circular flow known as a convection current. The cycle is regulated by a built-in thermostat in each unit.
You can put these units in every room of the house if you want, but it’s more common for an electric baseboard to provide supplemental heat for individual rooms on an as-needed basis.
While electric baseboards are inexpensive, they are usually known to be inefficient, which means they can end up being more expensive in the long run. Because of this, many homeowners choose not to rely on electric baseboard heating units as their only home heating solution.
Hydronic baseboard units work similarly in that electricity still generates the system’s heat, however it does so indirectly. The electrical current warms up an enclosed fluid (oil or water), then that fluid radiates heat into the room where the unit has been installed.
Hydronic baseboard heating systems operate more efficiently because once the fluid has been warmed, it takes longer to cool down, therefore saving energy.
Advantages
Baseboard heaters operate quietly and have a relatively low installation cost. They are easily cleaned and have a long lifespan, too.
Disadvantages
They take up space and are not the most aesthetically-pleasing option. Baseboard heaters can also get very hot to touch so the space around them needs to be cleared.
Finding the best heating system for your home can be difficult. To get detailed information, it's best to get in touch with a contractor like ECI Comfort.
If you live in the Delaware Valley/Greater Philadelphia area and would like to find comfort within your home, visit our website or give us a call at 215 - 245 - 3200.