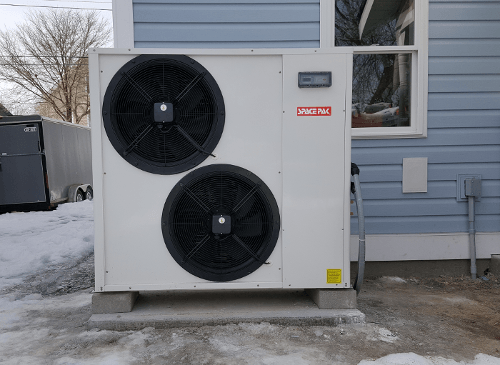
Between the initiative to move away from fossil fuels and the growing demand for high-performance, high-efficiency systems, heat pumps are quickly becoming the go-to for both residential and commercial systems. In an article from Plumbing & Mechanical Magazine, Ian McIver, product manager for Bosch, stated that "people are turning away from fossil fuels...and moving more toward heat pump systems simply because they are so much more efficient." Hydronic heat pumps, specifically, have begun to take the HVAC industry by storm as they start to replace traditional boiler systems.
What is a Hydronic Heat Pump?
So, what exactly is a hydronic heat pump? Heat pumps come in three forms: air-source, water-source, and geothermal -- all of which run on electricity. The most common type of heat pump is the air-source heat pump, which can be either air-to-air or air-to-water.
Air-to-air heat pump
Air-to-air heat pumps, commonly in the form of ductless heat pumps, work by absorbing thermal energy from the outside air and sending it inside to heat your home. In warmer seasons, the system extracts warm air from your home and sends it outside to provide cooling.
Air-to-water (hydronic) heat pump
Air-to-water heat pumps, known as hydronic heat pumps, rely on the same principles. However, instead of pushing tempered air through the home, hydronic heat pumps will use the outdoor heat energy to heat water. The warm water is then sent through tubing in the floor or baseboards that release the heat in each room, or through pipes to provide domestic hot water.
When you need to cool the home, the system works to draw heat from inside the home and send it over the coils where it is cooled and then sent back through the home.
Check out this diagram from Mitsubishi Electric's website:

Benefits of Hydronic Heat Pumps
Efficiency
Because heat pumps move heat rather than create heat, they can transfer 300 percent more energy than they consume. Using water to heat your home requires less energy and provides higher efficiency than traditional HVAC systems. A hydronic heat pump system can also significantly reduce or completely eliminate your use of fossil fuels.

When compared to air-air heat pump systems, hydronic heat pumps have 16 times more carrying capacity, meaning they can be even more efficient. Mark Chaffee, a VP for Taco Comfort Solutions, explains the comparison: "Think about when you warm up your oven to 150° F to keep a plate of pancakes warm — you can stick your hand inside and wave it around. You are going to notice it is warm, but that’s it. When you stick your hand in 150° water and swish it around, you’re going to the hospital after about a few seconds. Water is a much better, far more efficient and environmentally-friendly way to transfer BTU when heating and cooling."
Zoning ability
These systems have highly flexible designs and can be used for many different applications. They are also flexible in regards to installation and can be used to create zones in the home. Zoning allows for more precise temperature control and higher efficiency, which leads to energy bill savings. According to Jason Abajian, North America water sales manager for Resideo, businesses and multifamily complexes are among the most popular candidates for heat pump systems. The ability to create personalized comfort while saving energy and money makes it a great option for those looking to heat/cool several areas.
Heating and cooling

Finally, heat pumps have the ability to both heat and cool your home. A heat pump can be used as your only HVAC system, or it can supplement existing heating and cooling. Either way, you will be able to save energy and money while using a more environmentally friendly solution.
Limitations of Hydronic Heat Pumps
Lower heating energy
Since current heat pumps can only produce water temperatures around 125-130 degrees, they cannot yet completely replace a conventional fossil fuel boiler in a system that may require temperatures upwards of 180 degrees. But heat pumps can still provide the majority of the seasonal heating energy needed and can be supplemented by a new or existing boiler.
Outdated electrical grid
There is also the issue of the outdated U.S. electrical grid needing expanded capacity. Since the demand for heat pumps is on the rise, the grid will need to be upgraded to accommodate these potential electrical loads.
Higher upfront cost
Heat pumps call for a higher upfront cost compared to traditional systems. With this being said, many areas offer rebates and incentives for these high-efficiency systems. This efficiency also results in higher savings over time, making heat pumps a good long-term investment.
The Future of Hydronic Heat Pumps
Air-to-water heat pumps are expected to follow the trend of air-to-air ductless heat pumps in that they will continue to grow in popularity. As fossil fuel costs continue to increase, the energy cost savings associated with hydronic heat pumps will become more attractive to homeowners. The growing concern for climate change is also causing more people to think about replacing their traditional boilers with hydronic heat pumps.
If you live in the Delaware Valley/Greater Philadelphia area and would like to find comfort within your home, visit our website or give us a call at 215 - 245 - 3200 to learn more.