Boilers come in many forms and have several moving parts. From steam and hot water, to fire-tube and water-tube, to the different fuel sources, we'll go over some boiler basics so that you can better understand your home heating system.
How Do Boiler Systems Work?
A boiler is a popular type of central heating system that burns fuel or uses electricity to heat water. Hot water is sent as is or in the form of steam to pipes throughout the house to provide heat to radiators or radiant floor systems.
Both steam and hot water boilers can be fueled by oil, gas, or electricity. All boilers are either condensing or non-condensing.
Steam boilers
Steam boilers use a heat exchanger to heat water to a boiling point and distribute it as steam to a piped system that connects around the home. These boilers have to work at a higher temperature than hot water boilers, but use less energy during the transfer of heat. The hot steam is sent to the radiators, then cooled condensation is sent back to the boiler to be reheated. Here's how it works in more detail:
First, the boiler is partially filled with the water which is heated and turned into steam. The pressure within the system increases to send steam through the pipes up into the radiators. As the pressure increases, an air vent within the radiator(s) opens. When the steam reaches the vent, the vent closes and the head of the radiator radiates heat into the room. The steam then cools and condenses back into water that's sent back to the boiler to be reheated.
Steam boilers are usually found in older homes.
Hot water boilers
Hot water boilers also use a heat exchanger to heat water just until it's hot enough, which is then distributed to a piped system. A hot water boiler uses less energy to create hot water, but more energy during the transfer of heat. Hot water boilers can work with both radiators and radiant floor systems, like hydronic radiant flooring. Here's how it works in more detail:
First, the thermostat calls for heat. An oil or gas burner is then activated, heating the water in the boiler. The pumps will either begin pumping water through the system, or wait for the water heater to pre-heat to the desired temperature. The heated water expands and extra volume is sent into the expansion tank. The heat then radiates from the hot water in the radiators. Next, the water cools and is sent back to the boiler via gravity or a separate pump to be reheated.
Hot water boilers are typically found in newer homes and are second in popularity to forced-air systems.
Fire-tube versus water-tube boilers
Put simply, in a fire-tube boiler (top), the fire or hot gas is present inside the tubes with water surrounding the fire tubes. In a water-tube boiler (bottom), the water is present inside the tubes, and fire or hot gases surround these fire tubes.
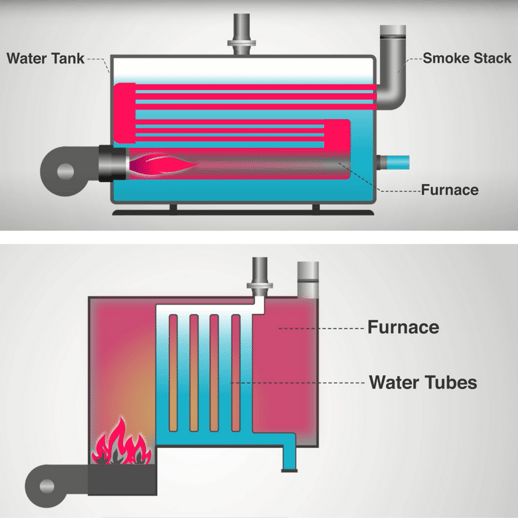
In a fire-tube boiler, fuel is burned inside the furnace, then the tube transfers the heat of the furnace through the water in the tank. Fire-tube boilers tend to be the cheapest to produce due to their relatively simple construction, but are typically limited to low to medium pressure applications.
A water-tube boiler is similar, but instead of the furnace heating fire tubes to heat water in the tank, the furnace directly heats water tubes inside of the furnace. This type of boiler is the more efficient option.
Types of Boilers
Water can't be heated without a heat source, which brings us to the three main types of boilers: oil, gas, and electric.
Oil-fired boilers
Oil-fired boilers require a separate oil tank that pumps oil to your boiler. The oil is used to heat the water and send steam or hot water throughout the piping in your home. Oil heating systems are common where natural gas is limited, but they can be more expensive due to the associated costs of volatile oil prices.
Gas-fired boilers
Gas-fired boilers can use natural gas or propane. Propane is stored in a tank and is a good alternative if you don't live in an area with natural gas lines. However, propane can be more expensive. Natural gas is typically pumped through a gas line underneath the house via a pipeline from an adjacent road. The gas is used to keep a pilot light lit, which warms the heating coils in the boiler, passing along the heat to the water in the tank. Newer gas boilers are highly efficient.
Electric boilers
Electric boilers do not rely on fossil fuels and are the most energy-efficient type of boiler. Because they don't rely on gas or fuel supply, electric boilers are convenient for rural households. They are also quieter and take up less space. On the other hand, losing electricity means you would also lose heat if you don't have a backup generator. Electricity is generally more expensive than fuel as well.
Combination (Combi) Boilers
A combi boiler can provide both heating and hot water all in one, making it an efficient and space-saving option. Less equipment also reduces installation costs which, paired with higher efficiency, will save you money overall.
One example of a combi boiler is the Lochinvar NOBLE, which provides plentiful hot water, operates quietly, and has advanced electronic control.
If you live in the Delaware Valley/Greater Philadelphia area and would like to find comfort within your home, visit our website or give us a call at 215 - 245 - 3200.