There are many options to consider when choosing the right type of home heating system, and one major factor to consider in this decision is efficiency. Energy efficiency is becoming more and more important when it comes to home HVAC systems. Plus, lower energy usage translates to lower electricity bills, so it's definitely something to be considered.
So how do different systems -- specifically heat pumps, gas furnaces, and radiators -- compare?
How Do They Work?
Heat pumps
Heat pumps work similarly to refrigerators as they use electricity to move heat from a cold space to a warm space. For heating, heat pumps will take the heat from outside your home and move it to that refrigerant coolant. The coolant is then moved to the indoor unit of the heat pump, which compresses air that passes over the hot coolant, and provides heat for your home during those cold winter days! For cooling, the air is pulled in from outside your home and is passed over condenser and evaporator coils for expansion. The air cools down and the refrigerant heats up. The air is then ready to be pushed out to cool your home.
Ducted heat pumps send the air through smaller ductwork to be distributed through the home, while ductless heat pumps send the air through small line sets in the wall that connect directly to an air handler in each room.

Gas furnaces
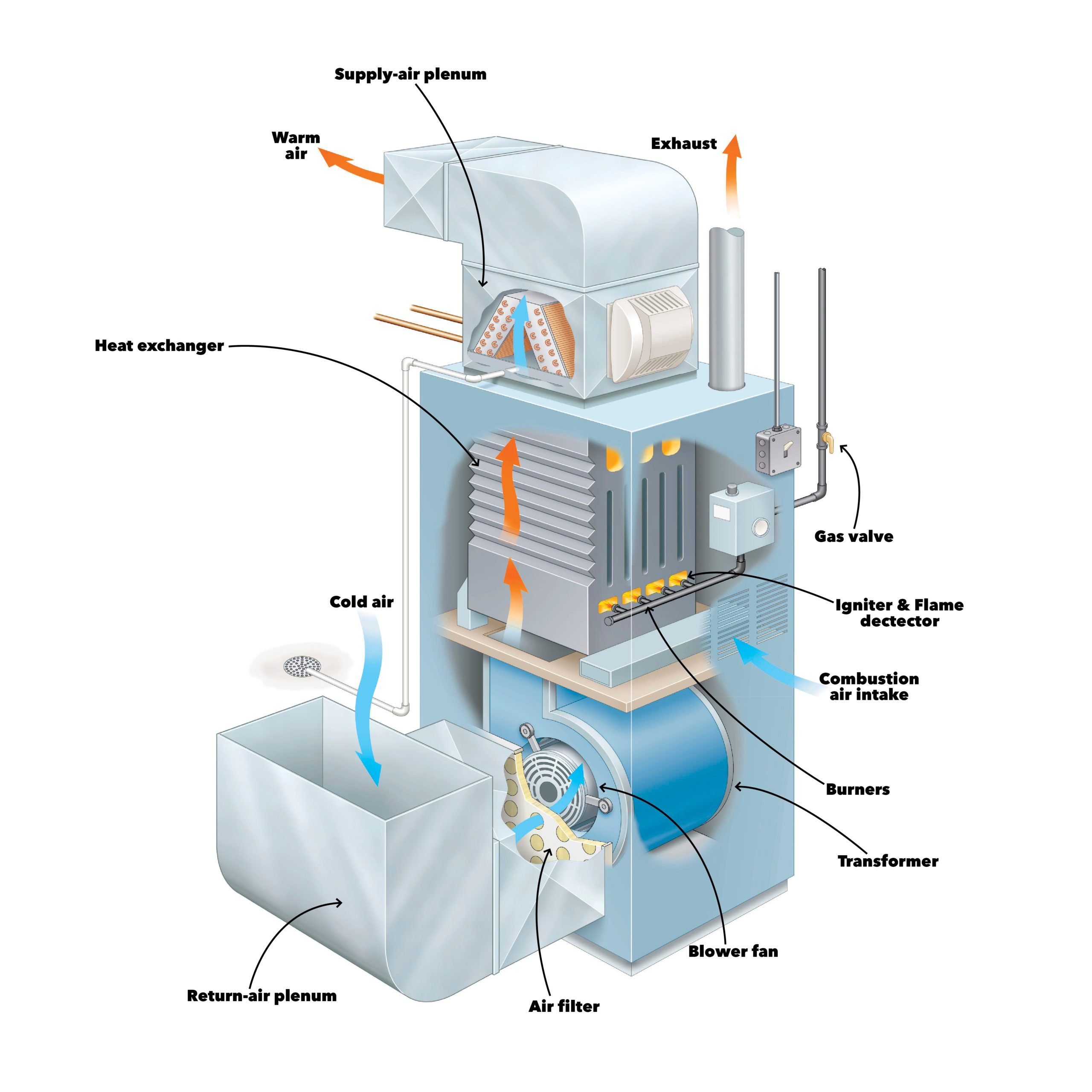
Gas furnaces work simply by the burning of propane, natural gas, or oil to create heat. The heat that is produced is then passed through a metal heat exchanger in the furnace. This heat is then blown into the ductwork and passed throughout your home, which is why they are considered forced-air systems. As warm air is filling each room, cold air is being sucked into the furnace through return ducts. This process is a continuous cycle and is how furnaces provide heating for your home. Gas furnaces also work hand in hand with air conditioners, as when it's hot outside, an air conditioner will disable the heating part of a furnace and use the air the furnace sucks in from outside to cool your home.
Radiators
Classic cast-iron radiators work by converting water into steam, then transferring heat into the air through radiation and convection. Two of the most current types of radiators include the hot-water baseboard radiator (right) and panel radiator (left) which both run from hot-water systems, with the panel radiator also offering electric models. The hot-water baseboard radiator contains a boiler system that transfers heat from the water into the radiators. The room that the radiator is in is then heated through the transfer of heat from the radiator to the air, using convection.
The panel radiator is made up of steel panels and is hung from the wall in most cases. It contains fins that control the amount of heat transferred into the air. Airflow is by convection only and it is around the radiator. If you are looking to replace your older radiator or are curious about modern radiators, click here to learn more.

How Does the Efficiency Compare?
Heat pumps
When looking at efficiency for heat pumps, know that they are powered by electricity, and because of this, sustainability on fuel consumption can be saved. Only a small amount of electricity is needed to power the heat pump, which allows the heat pump to transfer more thermal energy in the form of heat than it consumes in electrical energy. On average, a heat pump can transfer around 300 percent more energy than it consumes, compared to a highly efficient gas furnace average of about 97 percent more than it consumes.
Heat pumps do not generate heat, rather, they move heat, which provides equivalent space conditioning at only one-quarter of the cost of operating conventional heating or cooling appliances. Heat pumps also have no standby loss, which means that they do not use any unnecessary energy or hot water to get the job done. Standby loss comes from energy wasted when water is always being heated in tanks and energy is always being used even when a hot water tap isn't running.
Radiators and gas furnaces, in comparison, can experience high degrees of standby loss (which also equates to higher costs). In addition, both radiators and gas furnaces are quite large in size and can be a problem for many homeowners, especially those in rowhomes or townhouses. Heat pumps will take up less space inside and outside your home, so if you live in a smaller home or need to conserve space, heat pumps would work best.
Ductless Heat Pumps
Ductless heat pumps can be even more efficient than ducted heat pumps as they provide zoned control. Zoned control allows you to control the temperature in every room/area that a unit is in. This allows your system to not waste too much energy, but instead use just enough for the room that a unit is in to be satisfied.
Ductless heat pump efficiency also saves money over time, with 60 percent of heating costs cut compared to electric resistance-based systems. Cooling costs are 30 percent less than traditional air conditioners as well. So if you're looking for even more efficiency, ductless heat pumps are the answer! Ductless heat pumps, however, have problems when air falls below 40 degrees. At this point, they may start to lose their efficiency and consume more unnecessary energy to do their job because they rely on the external air of your home to heat your home. So take note of this, but know that every type of system has its own risks and inefficiencies.
Luckily, there's the option of the Hyper-Heat heat pump from Mitsubishi that works up until temperatures reach negative 13 degrees.
Gas furnaces
Gas furnaces can be efficient in many ways and one of their strong attributes is that they are great for colder climates, as they are not dependent on external temperatures to rely on heat. It is important to know, though, that they can also run into some inefficiencies. As stated earlier, like radiators, furnaces tend to also be larger in size and can take up a lot of space, especially in rowhomes or townhouses. Gas furnaces can also short-cycle which is when a furnace unit turns on and off too frequently. This can be due to thermostat malfunctioning, overheating through a dirty filter and blocked exhaust vents, or an oversized/undersized unit. While this problem can be fixed, it is something that can go unnoticed for a long period of time, which can be costly.
Moreover, gas furnaces can sometimes overwork and generate too much energy to create heat for your home which creates standby loss. When working properly, however, many gas furnaces can use as high as 97 percent of the energy that they produce, which is near total efficiency.
Radiators
In terms of efficiency, like the other systems, radiators have their pros and cons. Radiators can be energy efficient when rooms are always set to the same temperature. This is from the unit recognizing the set temperature and adjusting itself to that constant temperature without wasting too much unnecessary energy. If the temperature is changed frequently, however, then efficiency can go down.
A radiator can oftentimes overwork itself due to the creation of unnecessary energy in the radiator that can be caused by excessive and wasted burning of hot water to create steam that results in standby loss. Another reason a radiator may overwork itself is from short-cycling, which can be caused when steam returns and pushes the air that the radiator has produced back into the radiator, where air cannot flow from the vents properly and pressure continues to build from this.
In Summary
Now that you have learned about gas furnaces, radiators, heat pumps and how efficient they can be, remember that they all have their specialties and can provide terrific heating and air for your home, especially heat pumps with zoned control and 300 percent more energy transferred than consumed due to electricity!
If you want to reduce or eliminate your use of fossil fuels, save energy and money, and invest in a system that provides heating and cooling, heat pumps are the perfect option.
But the best way to find the most suitable system for your home is to schedule a consultation with a professional contractor like ECI Comfort.
If you live in the Delaware Valley/Greater Philadelphia area and would like to find affordable comfort within your home, visit our website or give us a call at 215 - 245 - 3200 to learn more.